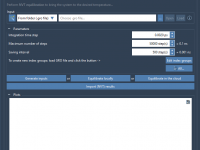
GROMACS Wizard – COM Pulling
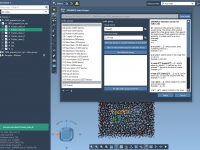
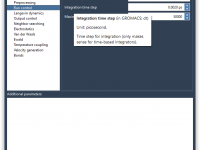
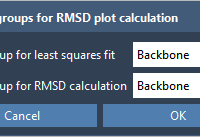
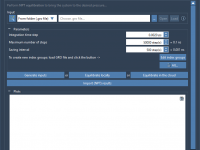
This section is a part of the GROMACS Wizard tutorial. This tutorial demonstrates how to perform COM Pulling using GROMACS Wizard. Reference: We will use the same system, 2BEG, as in the Umbrella Sampling tutorial by Justin A. Lemkul. 1. Loading the system First, load the system: go to Home menu > Fetch and load 2BEG from the RCSB PDB in mmCIF or PDB format. When loading the structure into SAMSON a pop-up might appear with import options depending on the…