Loading...
Searching...
No Matches
Node types
SAMSON Document are composed of nodes.
The image below shows some of the possible node types and their corresponding icons in the document view.
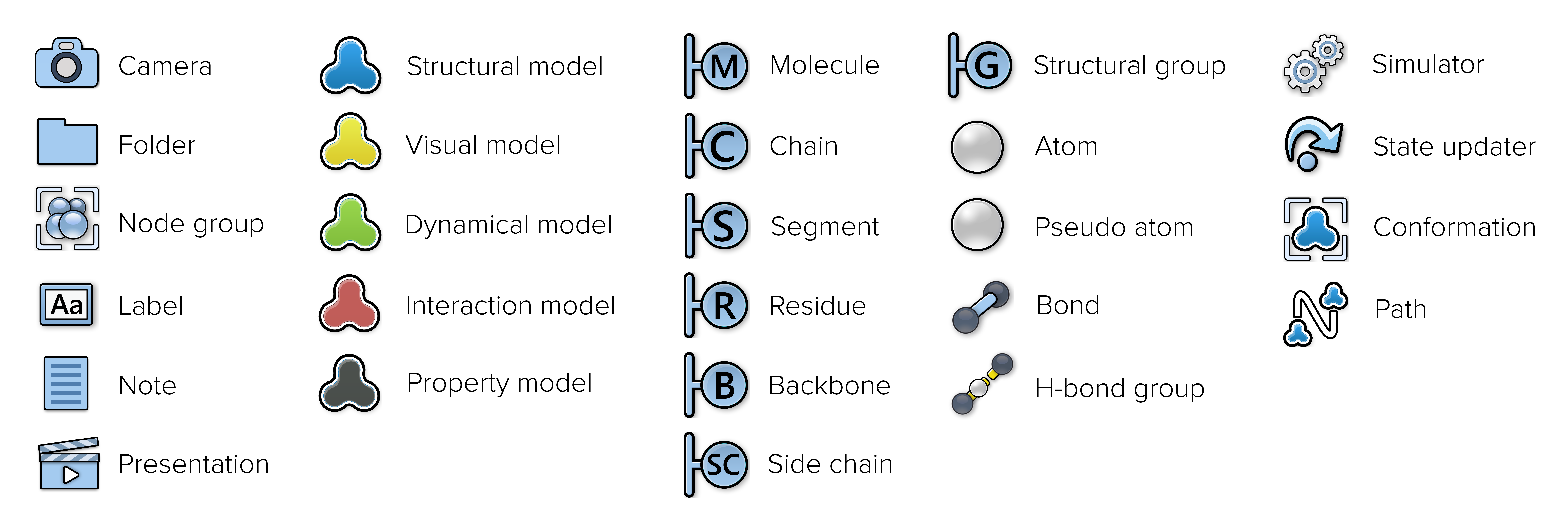
Document nodes
See also: Models
Hierarchy
SAMSON Documents have a hierarchical structure: each node has one and only one parent, and possibly some children or references to other nodes.
Nodes of a given type can only have children of some specific types:
- A document can contain the same node types as the folder, it is basically the root folder. Additionally, it can contain cameras.
- A folder can contain folders, files, Python scripts, structural models, visual models, dynamical models, interaction models, property models, simulators, labels, notes, render presets.
- A presentation contains animations.
- A structural model can contain atoms, backbones, bonds, chain, molecules, residues, segments, side chains, and structural groups.
- A structural group can contain atoms, backbones, bonds, chain, molecules, residues, segments, side chains, and structural groups.
- A molecule can contain structural groups, chains, segments, residues, atoms, and bonds.
- A chain can contain structural groups, segments, residues, atoms, and bonds.
- A segment can contain atoms, bonds, structural groups, and residues.
- A residue can contain a single backbone and a single side chain.
- A backbone can contain atoms and bonds.
- A side chain can contain atoms and bonds.
- A simulator can contain a state updater.
The following nodes cannot have children:
- Cameras
- visual models
- dynamical models
- interaction models
- property models
- state updaters
- conformations
- paths
- files
- scripts
- notes
- render presets
Nodes can also reference other nodes that are not their children:
- A bond references two atoms.
- A node group references the nodes contained in the group.
- A H-bond group contains H-bonds that reference two to three atoms (an acceptor, a donor, a hydrogen), but are not the parent of the referenced atoms.
- A conformation references a group of atoms with their position saved.
- A path is a trajectory of a group of atoms and references this group of atoms.
- A dynamical model references structural nodes.
- An interaction model references a dynamical model.
- A simulator references a dynamical model and an interaction model.
Some other types of nodes:
- A file represents any type of an embedded file, e.g. a PDF, an image, some data file, some structure file, etc., basically, any type of file.
- A script represents a Python script file, it can be opened via Code editor and launched using the integrated Python console.
- A note can contain text (including html), e.g. describing the current document, molecules, experiments, etc.
- A render preset contains rendering settings.

