SAMSON represents nanosystems using five categories of models:
 Structural models describe geometry and topology.
Structural models describe geometry and topology. Visual models provide graphical representations.
Visual models provide graphical representations. Dynamical models describe dynamical degrees of freedom.
Dynamical models describe dynamical degrees of freedom. Interaction models describe energies and forces.
Interaction models describe energies and forces. Property models describe properties that do not enter in the first four model categories.
Property models describe properties that do not enter in the first four model categories.
Apart from these models, SAMSON also has state updaters used in the minimization and simulations.
Models and state updaters are nodes in SAMSON Document.
See also: Node types
Structural models
![]() Structural models describe the geometry and topology of nanosystems in SAMSON. Typically, a structural model contains atoms and bonds, and might contain nodes representing higher organization levels, e.g. molecules, chains, residues, etc.
Structural models describe the geometry and topology of nanosystems in SAMSON. Typically, a structural model contains atoms and bonds, and might contain nodes representing higher organization levels, e.g. molecules, chains, residues, etc.
Visual models
![]() Visual models are used to provide graphical representations. A visual model may be e.g. a secondary structure representation of a protein, a gaussian surface, an isosurface of an electron density, a volumetric representation of an electrostatic field, etc.
Visual models are used to provide graphical representations. A visual model may be e.g. a secondary structure representation of a protein, a gaussian surface, an isosurface of an electron density, a volumetric representation of an electrostatic field, etc.
SAMSON provides a set of visual models by default and you can add more from SAMSON Connect (SAMSON Extensions may also provide visual models). You can see some of the default visual models supplied with SAMSON on the image below.
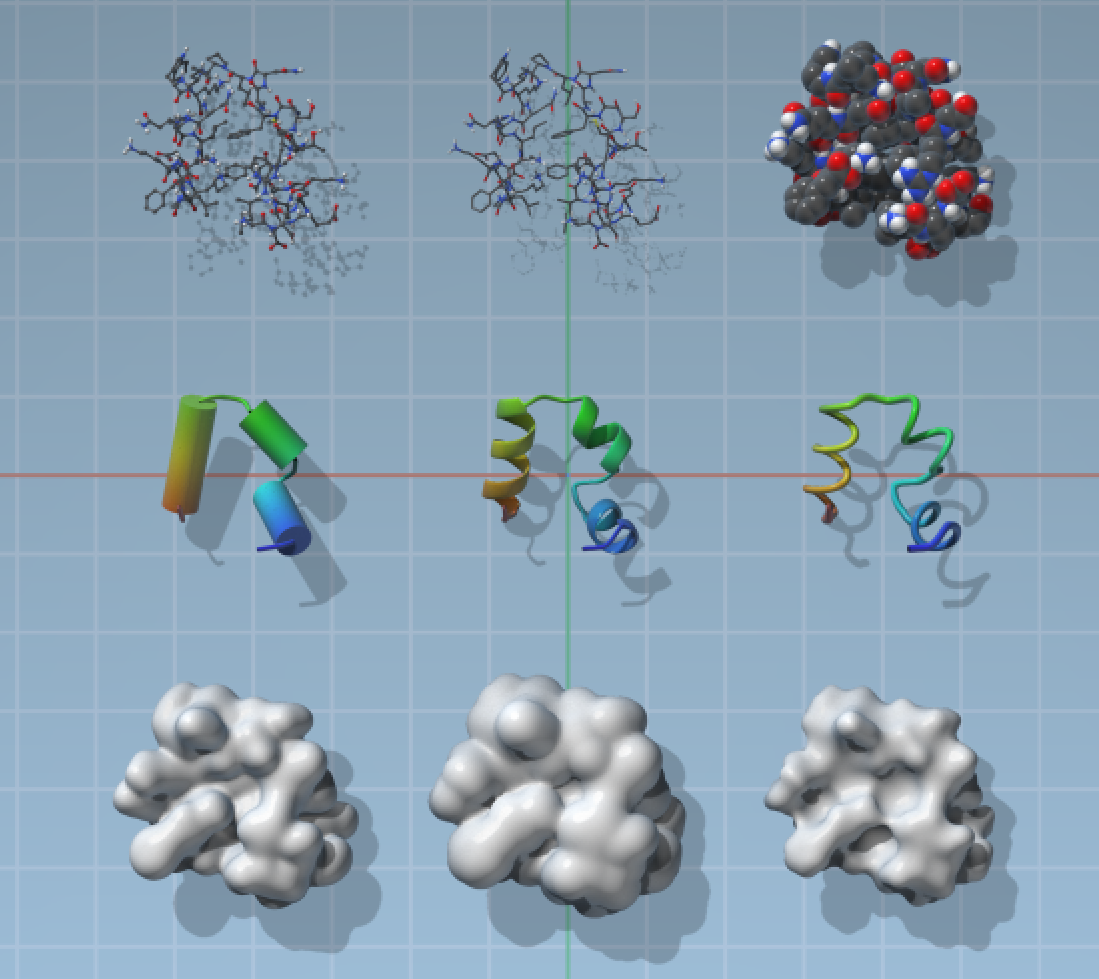
Visual models are usually applied to selected nodes or to the whole document if nothing is selected as follows:
- via the context toolbar menu of the selection
- using Visualization menu > Add > Visual model
- shortcut: Ctrl / Cmd⌘ + Shift + V
See the Visualizing section for more information on how to apply visual models.
For some visual models, you can modify their visualization parameters in the Inspector. For that, select the visual model in the document view and click on Inspect in the context menu.
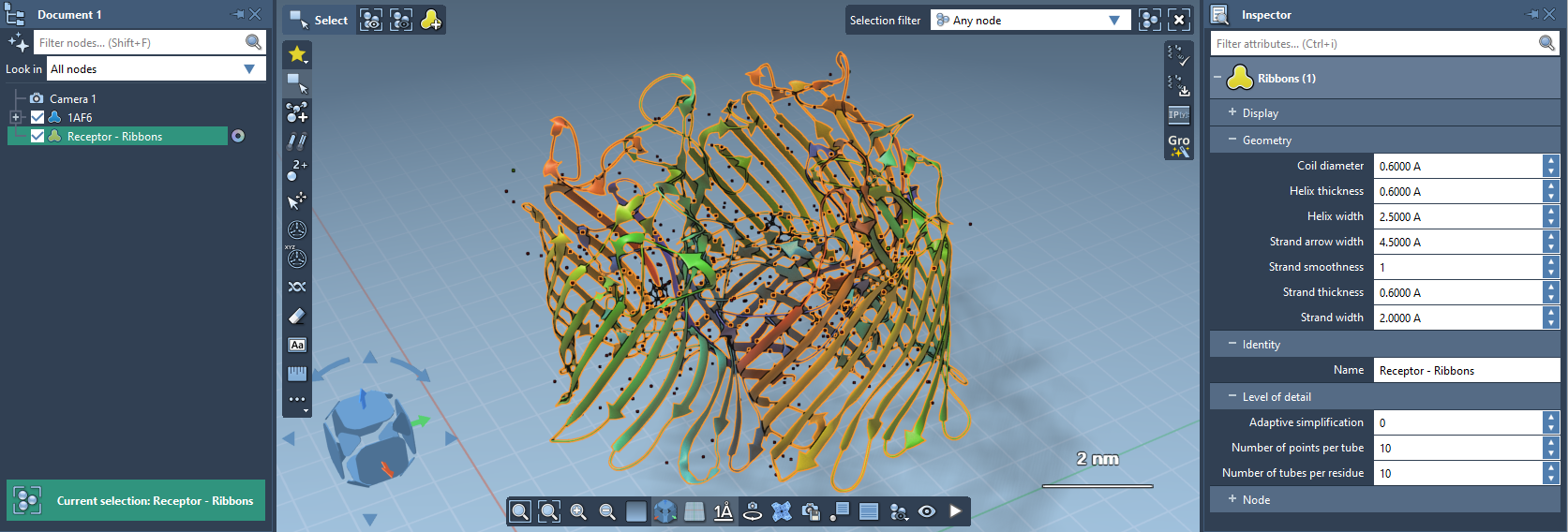
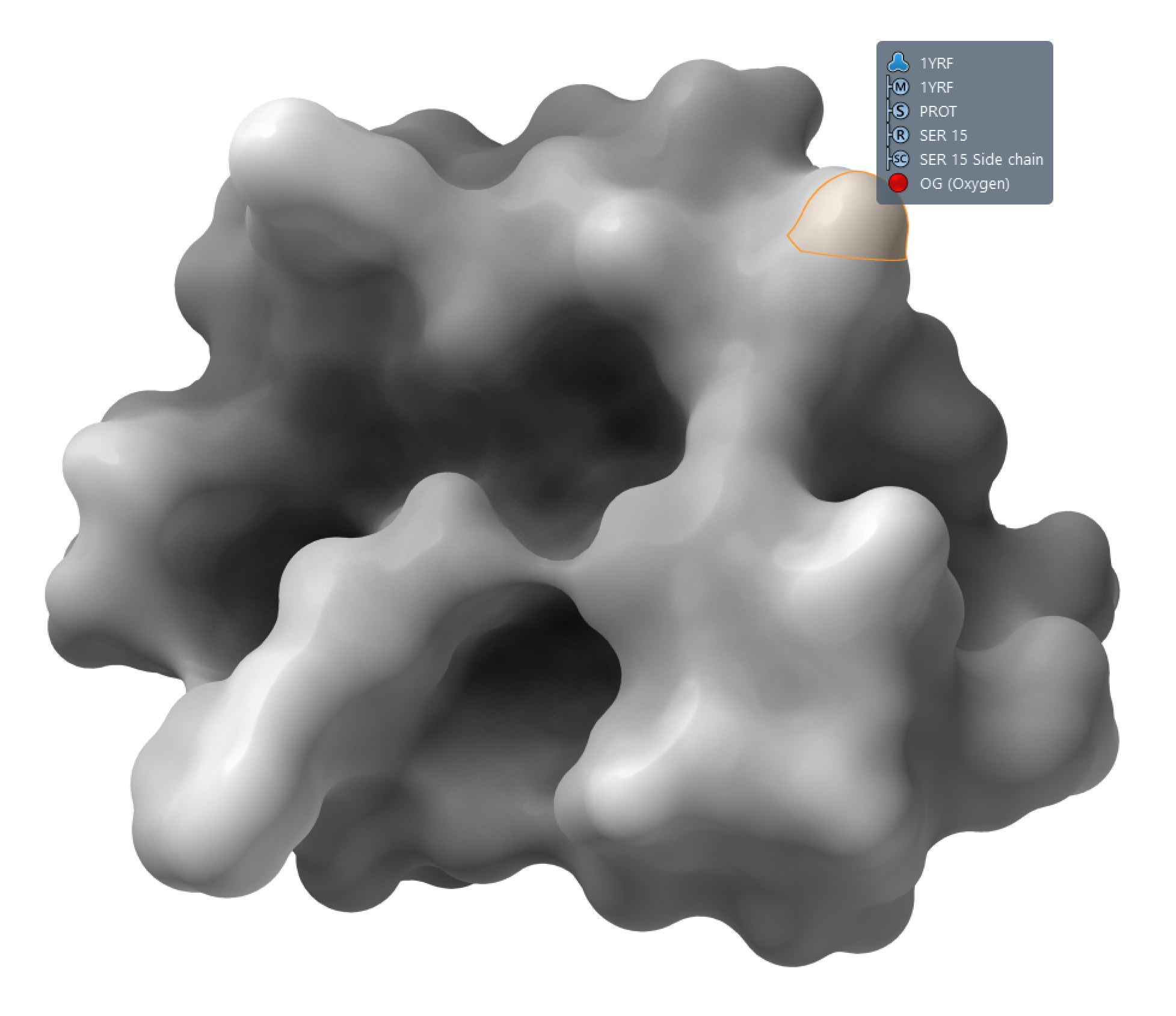
The default visual models in SAMSON make it possible to highlight and select atoms, residues, chains, etc. directly via surfaces depending on the current selection filter.
If you want to start developing you own visual models, please, refer to the documentation about generating SAMSON Extensions and the Documentation center for more information about writing new visual models for SAMSON.
See also: Visualizing, Color schemes, Visual presets, Presenting and animating
Dynamical models
![]() Dynamical models are used to indicate where degrees of freedom are in structural nodes. For example, a particle system dynamical model applied to a group of particles (atoms) assigns three translational degrees of freedom to each atom. Dynamical models describe the dynamical state and store positions, momenta, and masses.
Dynamical models are used to indicate where degrees of freedom are in structural nodes. For example, a particle system dynamical model applied to a group of particles (atoms) assigns three translational degrees of freedom to each atom. Dynamical models describe the dynamical state and store positions, momenta, and masses.
Interaction models
![]() Interaction models are used to represent energies and forces in a dynamical model and are used in SAMSON to perform various modeling and simulation tasks. An interaction model could be, for example, a simple Lennard-Jones model to describe unbounded interactions between a group of particles (atoms), a spring model, an elastic network model, a universal force field, etc.
Interaction models are used to represent energies and forces in a dynamical model and are used in SAMSON to perform various modeling and simulation tasks. An interaction model could be, for example, a simple Lennard-Jones model to describe unbounded interactions between a group of particles (atoms), a spring model, an elastic network model, a universal force field, etc.
An interaction model is in charge of providing forces corresponding to the degrees of freedom in a dynamical model. For example, an interaction model applied to a particle system dynamical model provides both the total energy of the particle system and the force applied to each particle (atom) in the particle system.
SAMSON provides a set of interaction models by default and you can add more from SAMSON Connect.
If you want to start developing you own interaction models, please, refer to the documentation about generating SAMSON Extensions and the Documentation center for more information about writing new interaction models for SAMSON.
Property models
![]() Property models are used to represent properties of nanosystems that are not already described by the first four categories of models. For example, property models may be e.g. a simple number describing the gyration radius of a protein, a scalar field (such as an electron density), a vector field (to represent e.g. an electrostatic field), a function, etc.
Property models are used to represent properties of nanosystems that are not already described by the first four categories of models. For example, property models may be e.g. a simple number describing the gyration radius of a protein, a scalar field (such as an electron density), a vector field (to represent e.g. an electrostatic field), a function, etc.
State updaters
![]() State updaters implement methods used to advance states during simulations. State updaters may be e.g. minimization algorithms, Monte Carlo methods, molecular dynamics algorithms, etc.
State updaters implement methods used to advance states during simulations. State updaters may be e.g. minimization algorithms, Monte Carlo methods, molecular dynamics algorithms, etc.
SAMSON provides a set of state updaters by default and you can add more from SAMSON Connect.
If you want to start developing you own state updaters, please, refer to the documentation about generating SAMSON Extensions and the Documentation center for more information about writing new state updaters for SAMSON.

